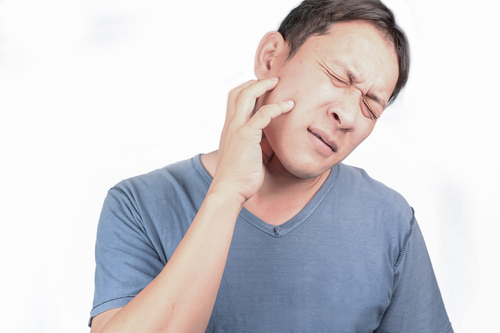
TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorder is a condition that affects the muscles and nerves of the temporomandibular joint. This joint is located on each side of the jaw and it connects the jaw to the skull. TMJ occurs when the muscles and nerves of the TMJ joint become injured or inflamed.
A TMJ disorder is extremely common (an estimated 12 percent of American’s suffer from the condition), and women are affected more than men. Determining the cause of TMJ can be challenging. There are several factors that can contribute to this disorder, including arthritis, genetics, habitual teeth grinding (bruxism), stress, diseases of the connective tissues, and injuries to the jaw. Whatever the cause, TMJ can be painful and in extreme cases, it can limit the ability to effectively operate the jaw.
There are several symptoms associated with TMJ disorder. If you experience any of the following symptoms, chances are you have TMJ.
1. Pain in the temporomandibular joint
Since TMJ disorder is a condition that affects the temporomandibular joint, it is no surprise that one of the most common symptoms is a pain in this joint. The temporomandibular joint is located on each side of the jaw, right in front of the ear. Every time you open and close your jaw, you have your TMJ joint to thank.
It acts as a sliding hinge of sorts, allowing the jaw to move. Since TMJ disorder affects the muscles and nerves of this joint, it makes sense that the condition will cause pain in the joint itself. The pain can range from mild to severe and can come and go. You might notice that it’s worse after eating or while you are talking. You could also experience more pain upon waking, which could be a sign that you grind your teeth while you sleep.


